Background: One of the smallest independent countries in the western hemisphere, Grenada was seized by a Marxist military council on 19 October 1983. Six days later the island was invaded by US forces and those of six other Caribbean nations, which quickly captured the ringleaders and their hundreds of Cuban advisers. Free elections were reinstituted the following year.
Government type: constitutional monarchy with Westminster-style parliament
Capital: Saint George’s
Currency: 1 East Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents
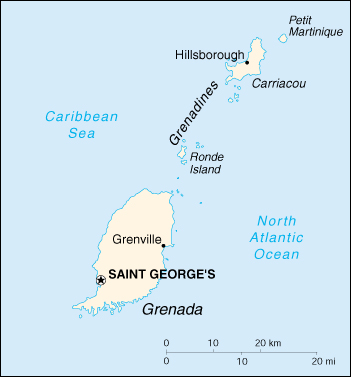
Geography of Grenada
Location: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Geographic coordinates: 12 07 N, 61 40 W
Area:
total: 340 sq. km
land: 340 sq. km
water: 0 sq. km
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 121 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical; tempered by northeast trade winds
Terrain: volcanic in origin with central mountains
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point: Mount Saint Catherine 840 m
Natural resources: timber, tropical fruit, deep-water harbors
Land use:
arable land: 15%
permanent crops: 18%
permanent pastures: 3%
forests and woodland: 9%
other: 55% (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: lies on edge of hurricane belt; hurricane season lasts from June to November
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography – note: the administration of the islands of the Grenadines group is divided between Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Grenada
People of Grenada
Most of Grenada’s population is of African descent; there is some trace of the early Arawak and Carib Indians. A few East Indians and a small community of the descendants of early European settlers reside in Grenada. About 50% of Grenada’s population is under the age of 30. English is the official language; only a few people still speak French patois. A more significant reminder of Grenada’s historical link with France is the strength of the Roman Catholic Church to which about 60% of Grenadians belong. The Anglican Church is the largest Protestant denomination.
Population: 89,502 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 37.05%
15-64 years: 59.03%
65 years and over: 3.92%
Population growth rate: -0.06%
Birth rate: 23.12 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 7.82 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: -15.86 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 14.63 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 64.52 years
male: 62.74 years
female: 66.31 years
Total fertility rate: 2.54 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Grenadian(s)
adjective: Grenadian
Ethnic groups: black 82% some South Asians (East Indians) and Europeans, trace Arawak/Carib Amerindian
Religions: Roman Catholic 60%, Anglican, other Protestant
Languages: English (official), French patois
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 98%
male: 98%
female: 98% (1970 est.)
History of Grenada
Before the arrival of Europeans, Grenada was inhabited by Carib Indians who had driven the more peaceful Arawaks from the island. Columbus landed on Grenada in 1498 during his third voyage to the new world. He named the island “Concepcion.” The origin of the name “Grenada” is obscure, but it is likely that Spanish sailors renamed the island for the city of Granada. By the beginning of the 18th century, the name “Grenada,” or “la Grenade” in French, was in common use.
Partly because of the Caribs, Grenada remained uncolonized for more than 100 years after its discovery; early English efforts to settle the island were unsuccessful. In 1650, a French company founded by Cardinal Richelieu purchased Grenada from the English and established a small settlement. After several skirmishes with the Caribs, the French brought in reinforcements from Martinique and defeated the Caribs the last of whom leaped into the sea rather than surrender.
The island remained under French control until its capture by the British in 1762, during the Seven Years’ War. Grenada was formally ceded to Great Britain in 1763 by the Treaty of Paris. Although the French regained control in 1779, the island was restored to Britain in 1783 by the Treaty of Versailles. Although Britain was hard pressed to overcome a pro-French revolt in 1795 Grenada remained British for the remainder of the colonial period.
During the 18th century, Grenada’s economy underwent an important transition. Like much of the rest of the West Indies it was originally settled to cultivate sugar which was grown on estates using slave labor. But natural disasters paved the way for the introduction of other crops. In 1782, Sir Joseph Banks, the botanical adviser to King George III, introduced nutmeg to Grenada. The island’s soil was ideal for growing the spice and because Grenada was a closer source of spices for Europe than the Dutch East Indies the island assumed a new importance to European traders.
The collapse of the sugar estates and the introduction of nutmeg and cocoa encouraged the development of smaller land holdings, and the island developed a land-owning yeoman farmer class. Slavery was outlawed in 1834. In 1833, Grenada became part of the British Windward Islands Administration. The governor of the Windward Islands administered the island for the rest of the colonial period. In 1958, the Windward Islands Administration was dissolved, and Grenada joined the Federation of the West Indies. After that federation collapsed in 1962, the British Government tried to form a small federation out of its remaining dependencies in the Eastern Caribbean.
Following the failure of this second effort, the British and the islands developed the concept of associated statehood. Under the Associated Statehood Act of 1967 Grenada was granted full autonomy over its internal affairs in March 1967. Full independence was granted on February 7, 1974.
After obtaining independence, Grenada adopted a modified Westminster parliamentary system based on the British model with a governor general appointed by and representing the British monarch (head of state) and a prime minister who is both leader of the majority party and the head of government. Sir Eric Gairy was Grenada’s first prime minister.
On March 13, 1979, the new joint endeavor for welfare, education, and liberation (New Jewel) movement ousted Gairy in a nearly bloodless coup and established a people’s revolutionary government (PRG), headed by Maurice Bishop who became prime minister. His Marxist-Leninist government established close ties with Cuba, the Soviet Union, and other communist bloc countries.
In October 1983, a power struggle within the government resulted in the arrest and subsequent murder of Bishop and several members of his cabinet by elements of the people’s revolutionary army. Following a breakdown in civil order, a U.S.-Caribbean force landed on Grenada on October 25 in response to an appeal from the governor general and to a request for assistance from the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States. U.S. citizens were evacuated, and order was restored.
An advisory council named by the governor general administered the country until general elections were held in December 1984. The New National Party (NNP) led by Herbert Blaize won 14 out of 15 seats in free and fair elections and formed a democratic government. Grenada’s constitution had been suspended in 1979 by the PRG but it was restored after the 1984 elections.
The NNP continued in power until 1989 but with a reduced majority. Five NNP parliamentary members, including two cabinet ministers, left the party in 1986-87 and formed the National Democratic Congress (NDC) which became the official opposition.
In August 1989, Prime Minister Blaize broke with the NNP to form another new party, The National Party (TNP), from the ranks of the NNP. This split in the NNP resulted in the formation of a minority government until constitutionally scheduled elections in March 1990. Prime Minister Blaize died in December 1989 and was succeeded as prime minister by Ben Jones until after the elections.
The NDC emerged from the 1990 elections as the strongest party, winning seven of the 15 available seats. Nicholas Brathwaite added two TNP members and one member of the Grenada United Labor Party (GULP) to create a 10-seat majority coalition. The governor general appointed him to be prime minister.
In parliamentary elections on June 20, 1995, the NNP won eight seats and formed a government headed by Dr. Keith Mitchell. The NNP maintained and affirmed its hold on power when it took all 15 parliamentary seats in the January 1999 elections.
Grenada Economy
Economy – overview: In this island economy progress in fiscal reforms and prudent macroeconomic management have kept annual growth steady since 1998. The increase in economic activity has been led by construction and trade. Tourist facilities are being expanded; tourism is the leading foreign exchange earner. Major short-term concerns are the rising fiscal deficit and the deterioration in the external account balance. Grenada shares a common central bank and a common currency with seven other members of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
GDP: purchasing power parity – $394 million (2000 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: 7% (2000 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $4,400 (2000 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 9.7%
industry: 15%
services: 75.3% (1996 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 2.5% (2000 est.)
Labor force: 42,300 (1996)
Labor force – by occupation: services 62%, agriculture 24%, industry 14% (1999 est.)
Unemployment rate: 15% (1997)
Budget:
revenues: $85.8 million
expenditures: $102.1 million, including capital expenditures of $28 million (1997)
Industries: food and beverages, textiles, light assembly operations, tourism, construction
Industrial production growth rate: 0.7% (1997 est.)
Electricity – production: 120 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1999)
Agriculture – products: bananas, cocoa, nutmeg, mace, citrus, avocados, root crops, sugarcane, corn, vegetables
Exports: $62.3 million (2000 est.)
Exports – commodities: bananas, cocoa, nutmeg, fruit and vegetables, clothing, mace
Exports – partners: Caricom 32.3%, UK 20%, US 13%, Netherlands 8.8% (1991)
Imports: $217.5 million (2000 est.)
Imports – commodities: food, manufactured goods, machinery, chemicals, fuel (1989)
Imports – partners: US 31.2%, Caricom 23.6%, UK 13.8%, Japan 7.1% (1991)
Debt – external: $89.2 million (1998)
Economic aid – recipient: $8.3 million (1995)
Currency: East Caribbean dollar (XCD)
Map of Grenada