Background: Guam was ceded to the US by Spain in 1898. Captured by the Japanese in 1941, it was retaken by the US three years later. The military installation on the island is one of the most strategically important US bases in the Pacific.
Dependency status: organized, unincorporated territory of the US with policy relations between Guam and the US under the jurisdiction of the Office of Insular Affairs, US Department of the Interior.
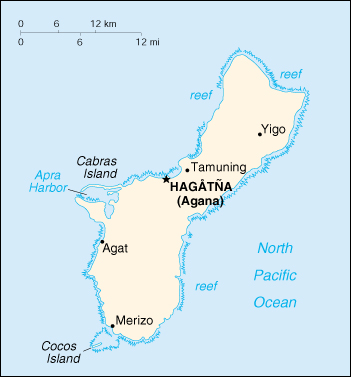
Capital: Hagatna (Agana)
Currency: 1 United States dollar (US$) = 100 cents
Geography of Guam
Location: Oceania, island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines
Geographic coordinates: 13 28 N, 144 47 E
Area:
total: 541.3 sq. km
land: 541.3 sq. km
water: 0 sq. km
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 125.5 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical marine; generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds; dry season from January to June, rainy season from July to December; little seasonal temperature variation
Terrain: volcanic origin, surrounded by coral reefs; relatively flat coralline limestone plateau (source of most fresh water), with steep coastal cliffs and narrow coastal plains in north, low-rising hills in center, mountains in south
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Lamlam 406 m
Natural resources: fishing (largely undeveloped), tourism (especially from Japan)
Land use:
arable land: 11%
permanent crops: 11%
permanent pastures: 15%
forests and woodland: 18%
other: 45% (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: frequent squalls during rainy season; relatively rare, but potentially very destructive typhoons (especially in August)
Environment – current issues: extirpation of native bird population by the rapid proliferation of the brown tree snake, an exotic species
Geography – note: largest and southernmost island in the Mariana Islands archipelago; strategic location in western North Pacific Ocean
People of Guam
Population: 168,564 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 35.07%
15-64 years: 58.78%
65 years and over: 6.15%
Population growth rate: 2.09%
Birth rate: 25.07 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 4.2 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 6.71 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 77.94 years
male: 75.66 years
female: 80.55 years
Total fertility rate: 3.85 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Guamanian(s)
adjective: Guamanian
Ethnic groups: Chamorro 47%, Filipino 25%, white 10%, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and other 18%
Religions: Roman Catholic 85%, other 15% (1999 est.)
Languages: English, Chamorro, Japanese
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99%
male: 99%
female: 99% (1990 est.)
Guam Economy
Economy – overview: The economy depends mainly on United States military spending, tourism, and the export of fish and handicrafts. Total US grants, wage payments, and procurement outlays amounted to $1 billion in 1998. Over the past 20 years, the tourist industry has grown rapidly, creating a construction boom for new hotels and the expansion of older ones. More than 1 million tourists visit Guam each year. The industry has recently suffered setbacks because of the continuing Japanese slowdown; the Japanese normally make up almost 90% of the tourists. Most food and industrial goods are imported. Guam faces the problem of building up the civilian economic sector to offset the impact of military downsizing.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $3.2 billion (2000 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $21,000 (2000 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
industry: 15% (1993)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 0% (1999 est.)
Labor force: 60,000 (2000 est.)
Labor force – by occupation: federal and territorial government 26%, private 74% (trade 24%, other services 40%, industry 10%) (2000 est.)
Unemployment rate: 15% (2000 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $605.3 million
expenditures: $654.2 million (2000)
Industries: US military, tourism, construction, transshipment services, concrete products, printing and publishing, food processing, textiles
Electricity – production: 800 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1998)
Agriculture – products: fruits, copra, vegetables; eggs, pork, poultry, beef
Exports: $75.7 million (f.o.b., 1999)
Exports – commodities: mostly transshipments of refined petroleum products; construction materials, fish, food and beverage products
Exports – partners: US 25%
Imports: $203 million (f.o.b., 1999 est.)
Imports – commodities: petroleum and petroleum products, food, manufactured goods
Imports – partners: US 23%, Japan 19%
Economic aid – recipient: Guam receives large transfer payments from the US Federal Treasury ($143 million in 1997) into which Guamanians pay no income or excise taxes; under the provisions of a special law of Congress, the Guam Treasury, rather than the US Treasury, receives federal income taxes paid by military and civilian Federal employees stationed in Guam
Currency: US dollar (USD)
Map of Guam