Background: International recognition of The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia’s (FYROM) independence from Yugoslavia in 1991 was delayed by Greece’s objection to the new state’s use of what it considered a Hellenic name and symbols. Greece finally lifted its trade blockade in 1995, and the two countries agreed to normalize relations, despite continued disagreement over FYROM’s use of “Macedonia.” FYROM’s large Albanian minority and the de facto independence of neighboring Kosovo continue to be sources of ethnic tension.
Government type: emerging democracy
Capital: Skopje
Currency: 1 Macedonian denar (MKD) = 100 deni
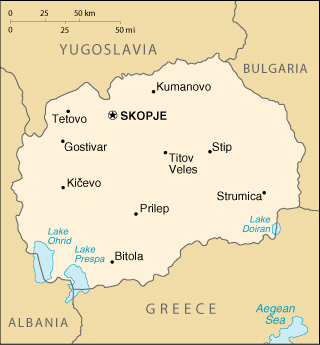
Geography of Macedonia
Location: Southeastern Europe, north of Greece
Geographic coordinates: 41 50 N, 22 00 E
Area:
total: 25,333 sq km
land: 24,856 sq km
water: 477 sq km
Land boundaries:
total: 748 km
border countries: Albania 151 km, Bulgaria 148 km, Greece 228 km, Serbia and Montenegro 221 km (all with Serbia)
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Climate: warm, dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy snowfall
Terrain: mountainous territory covered with deep basins and valleys; three large lakes, each divided by a frontier line; country bisected by the Vardar River
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Vardar River 50 m
highest point: Golem Korab (Maja e Korabit) 2,753 m
Natural resources: chromium, lead, zinc, manganese, tungsten, nickel, low-grade iron ore, asbestos, sulfur, timber, arable land
Land use:
arable land: 24%
permanent crops: 2%
permanent pastures: 25%
forests and woodland: 39%
other: 10% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 830 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: high seismic risks
Environment – current issues: air pollution from metallurgical plants
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography – note: landlocked; major transportation corridor from Western and Central Europe to Aegean Sea and Southern Europe to Western Europe
People of Macedonia
Population: 2,045,262 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 22.92%
15-64 years: 66.94%
65 years and over: 10.14%
Population growth rate: 0.43%
Birth rate: 13.5 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 7.7 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: -1.54 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 12.95 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 74.02 years
male: 71.79 years
female: 76.43 years
Total fertility rate: 1.79 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Macedonian(s)
adjective: Macedonian
Ethnic groups: Macedonian 66.6%, Albanian 22.7%, Turkish 4%, Roma 2.2%, Serb 2.1%, other 2.4% (1994)
Religions: Macedonian Orthodox 67%, Muslim 30%, other 3%
Languages: Macedonian 70%, Albanian 21%, Turkish 3%, Serbo-Croatian 3%, other 3%
Macedonia Economy
Economy – overview: At independence in November 1991, Macedonia was the least developed of the Yugoslav republics, producing a mere 5% of the total federal output of goods and services. The collapse of Yugoslavia ended transfer payments from the center and eliminated advantages from inclusion in a de facto free trade area. An absence of infrastructure, UN sanctions on its largest market Yugoslavia, and a Greek economic embargo hindered economic growth until 1996. GDP has subsequently increased each year, rising by 5% in 2000. Successful privatization in 2000 boosted the country’s reserves to over $700 million. Also, the leadership demonstrated a continuing commitment to economic reform, free trade, and regional integration. Inflation jumped to 11% in 2000, largely due to higher oil prices.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $9 billion (2000 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: 5% (2000 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $4,400 (2000 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 12%
industry: 25%
services: 63% (2000)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 11% (2000 est.)
Labor force: 1 million (1999 est.)
Unemployment rate: 32% (2000)
Budget:
revenues: $1.06 billion
expenditures: $1 billion, including capital expenditures of $107 million (1996 est.)
Industries: coal, metallic chromium, lead, zinc, ferronickel, textiles, wood products, tobacco
Industrial production growth rate: 3% (2000)
Electricity – production: 6.395 billion kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 82.25%
hydro: 17.75%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1999)
Electricity – consumption: 5.992 billion kWh (1999)
Agriculture – products: rice, tobacco, wheat, corn, millet, cotton, sesame, mulberry leaves, citrus, vegetables; beef, pork, poultry, mutton
Exports: $1.4 billion (f.o.b., 2000 est.)
Exports – commodities: food, beverages, tobacco; miscellaneous manufactures, iron and steel
Exports – partners: Germany 22%, Yugoslavia 22%, US 12%, Greece 7%, Italy 6% (2000)
Imports: $2 billion (f.o.b., 2000 est.)
Imports – commodities: machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels; food products
Imports – partners: Germany 13%, Ukraine 13%, Russia 10%, Yugoslavia 8%, Greece 8% (2000)
Debt – external: $1.4 billion (2000)
Economic aid – recipient: $100 million from the EU (2000)
Currency: Macedonian denar (MKD)
Map of Macedonia