Background: Settled as early as 1000 B. C., Samoa was “discovered” by European explorers in the 18th century. International rivalries in the latter half of the 19th century were settled by an 1899 treaty in which Germany and the US divided the Samoan archipelago. The US formally occupied its portion – a smaller group of eastern islands with the excellent harbor of Pago Pago – the following year.
Government type: Territory of USA.
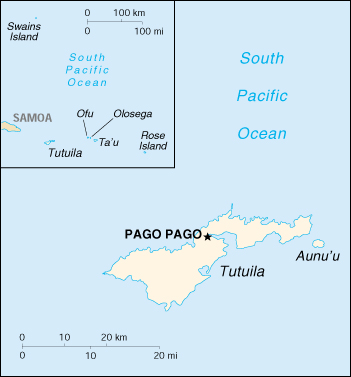
Capital: Pago Pago
Currency: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents
Geography of American Samoa
Location: Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about one-half of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand
Geographic coordinates: 14 20 S, 170 00 W
Area:
total: 199 sq. km
land: 199 sq. km
water: 0 sq. km
note: includes Rose Island and Swains Island
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 116 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical marine, moderated by southeast trade winds; annual rainfall averages about 3 m; rainy season from November to April, dry season from May to October; little seasonal temperature variation.
Terrain: five volcanic islands with rugged peaks and limited coastal plains, two coral atolls (Rose Island, Swains Island).
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Lata 966 m
Natural resources: pumice, pumicite
Land use:
arable land: 5%
permanent crops: 10%
permanent pastures: 0%
forests and woodland: 70%
other: 15% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: NA sq. km
Natural hazards: typhoons common from December to March
Environment – current issues: limited natural fresh water resources; the water division of the government has spent substantial funds in the past few years to improve water catchments and pipelines.
Geography – note: Pago Pago has one of the best natural deep-water harbors in the South Pacific Ocean, sheltered by shape from rough seas and protected by peripheral mountains from high winds; strategic location in the South Pacific Ocean.
People of American Samoa
Population: 177,287 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 38.44% (male 13,278; female 12,512)
15-64 years: 56.57% (male 18,784; female 19,163)
65 years and over: 4.99% (male 1,779; female 1,568)
Population growth rate: 2.42%
Birth rate: 24.88 births/1,000 population
Death rate:4.31 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: 3.58 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 10.36 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 75.32 years
male: 70.89 years
female: 80.02 years
Total fertility rate: 3.5 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: American Samoan(s)
adjective: American Samoan
Ethnic groups: Samoan (Polynesian) 89%, Caucasian 2%, Tongan 4%, other 5%
Religions: Christian Congregationalist 50%, Roman Catholic 20%, Protestant and other 30%
Languages: Samoan (closely related to Hawaiian and other Polynesian languages), English
note: most people are bilingual
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97%
male: 98%
female: 97% (1980 est.)
American Samoa Economy
Economy – overview: This is a traditional Polynesian economy in which more than 90% of the land is communally owned. Economic activity is strongly linked to the United States, with which American Samoa conducts the great bulk of its foreign trade. Tuna fishing and tuna processing plants are the backbone of the private sector, with canned tuna the primary export. Transfers from the United States Government add substantially to American Samoa’s economic well-being. Attempts by the government to develop a larger and broader economy are restrained by Samoa’s remote location, its limited transportation, and its devastating hurricanes. Tourism, a developing sector, may be held back by the current financial difficulties in East Asia.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $500 million (2000 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: NA%
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $8,000 (2000 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: NA%
industry: NA%
services: NA%
Population below poverty line: NA%
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA%
Inflation rate (consumer prices): NA%
Labor force: 13,949 (1996)
Labor force – by occupation: government 33%, tuna canneries 34%, other 33% (1990)
Unemployment rate: 16% (1993)
Budget:
revenues: $121 million (37% in local revenue and 63% in US grants)
expenditures: $127 million, including capital expenditures of $NA (FY96/97)
Industries: tuna canneries (largely dependent on foreign fishing vessels), handicrafts
Industrial production growth rate: NA%
Electricity – production: 130 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1999)
Electricity – consumption: 120.9 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – exports: 0 kWh (1999)
Electricity – imports: 0 kWh (1999)
Agriculture – products: bananas, coconuts, vegetables, taro, breadfruit, yams, copra, pineapples, papayas; dairy products, livestock
Exports:$500 million (1998)
Exports – commodities: canned tuna 93%
Exports – partners: US 99.6%
Imports: $471 million (1996)
Imports – commodities: materials for canneries 56%, food 8%, petroleum products 7%, machinery and parts 6%
Imports – partners: US 62%, Japan 9%, NZ 7%, Australia 11%, Fiji 4%, other 7%
Debt – external: $NA
Economic aid – recipient: $NA; note – important financial support from the US
Currency: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents
Map of American Samoa