Background
The Cayman Islands remained largely uninhabited until the 17th century. A variety of people settled on the islands: pirates, refugees from the Spanish Inquisition, shipwrecked sailors, deserters from Oliver Cromwell’s army in Jamaica, and slaves. The majority of Caymanians are of African and British descent, with considerable interracial mixing.
Great Britain took formal control of the Caymans, along with Jamaica, under the Treaty of Madrid in 1670. Following several unsuccessful attempts, permanent settlement of the islands began in the 1730s. The Cayman Islands historically have been popular as a tax haven. Legend has it that Caymanians in 1788 rescued the crews of a Jamaican merchant ship convoy which had struck a reef at Gun Bay and that the Caymanians were rewarded with King George III’s promise to never again impose any tax.
The Cayman Islands, initially administered as a dependency of Jamaica, became an independent colony in 1959; they now are a self-governing British Overseas Territory.
Government type: British crown colony
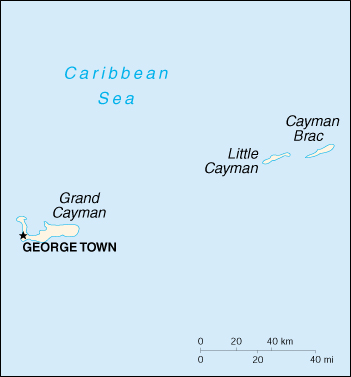
Capital: George Town
Currency: 1 Caymanian dollar (CI$) = 100 cents
Geography of Cayman Islands
Location: Caribbean, island group in Caribbean Sea, nearly one-half of the way from Cuba to Honduras
Geographic coordinates: 19 30 N, 80 30 W
Area:
total: 259 sq. km
land: 259 sq. km
water: 0 sq. km
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 160 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical marine; warm, rainy summers (May to October) and cool, relatively dry winters (November to April)
Terrain: low-lying limestone base surrounded by coral reefs
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point: The Bluff 43 m
Natural resources: fish, climate and beaches that foster tourism
Land use:
arable land: 0%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 8%
forests and woodland: 23%
other: 69% (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hurricanes (July to November)
Environment – current issues: no natural fresh water resources; drinking water supplies must be met by rainwater catchment
Geography – note: important location between Cuba and Central America
People of Cayman Islands
Population: 44,270 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 22.21%
15-64 years: 69.74%
65 years and over: 8.05%
Population growth rate: 2.12%
Birth rate: 13.79 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 5.15 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: 12.58 migrant(s)/1,000 population
note: major destination for Cubans trying to migrate to the US
Infant mortality rate: 10.16deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 79.03 years
male: 76.24 years
female: 81.43 years
Total fertility rate: 2.04 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Caymanian(s)
adjective: Caymanian
Ethnic groups: mixed 40%, white 20%, black 20%, expatriates of various ethnic groups 20%
Religions: United Church (Presbyterian and Congregational), Anglican, Baptist, Roman Catholic, Church of God, other Protestant
Languages: English
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over has ever attended school
total population: 98%
male: 98%
female: 98% (1970 est.)
Cayman Islands Economy
Economy – overview: With no direct taxation, the islands are a thriving offshore financial center. More than 40,000 companies were registered in the Cayman Islands as of 1997, including almost 600 banks and trust companies; banking assets exceed $500 billion. A stock exchange was opened in 1997. Tourism is also a mainstay, accounting for about 70% of GDP and 75% of foreign currency earnings. The tourist industry is aimed at the luxury market and caters mainly to visitors from North America. Total tourist arrivals exceeded 1.2 million visitors in 1997. About 90% of the islands’ food and consumer goods must be imported. The Caymanians enjoy one of the highest outputs per capita and one of the highest standards of living in the world.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $930 million (1997 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: 5% (1997 est.), 4.9% (1999 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $24,500 (1997 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 1.4%
industry: 3.2%
services: 95.4% (1994 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 3% (1998)
Labor force: 19,820 (1995)
Labor force – by occupation: agriculture 1.4%, industry 12.6%, services 86% (1995)
Unemployment rate: 4.1% (1997)
Budget:
revenues: $265.2 million
expenditures: $248.9 million, including capital expenditures of $NA (1997)
Industries: tourism, banking, insurance and finance, construction, construction materials, furniture
Electricity – production: 330 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1999)
Electricity – consumption: 306.9 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – exports: 0 kWh (1999)
Electricity – imports: 0 kWh (1999)
Agriculture – products: vegetables, fruit; livestock, turtle farming
Exports: $1.5 million (1998)
Exports – commodities: turtle products, manufactured consumer goods
Exports – partners: mostly United States
Imports: $507.6 million (1998)
Imports – commodities: foodstuffs, manufactured goods
Imports – partners: United States, Trinidad and Tobago, UK, Netherlands Antilles, Japan
Debt – external: $70 million (1996)
Currency: Caymanian dollar (KYD)
Map of Cayman Islands