Background: After almost four decades under US administration as the easternmost part of the UN Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, the Marshall Islands attained independence in 1986 under a Compact of Free Association. Compensation claims continue as a result of US nuclear testing on some of the islands between 1947 and 1962.
Government type: constitutional government in free association with the US; the Compact of Free Association entered into force 21 October 1986
Capital: Majuro
Currency: 1 United States dollar (US$) = 100 cents
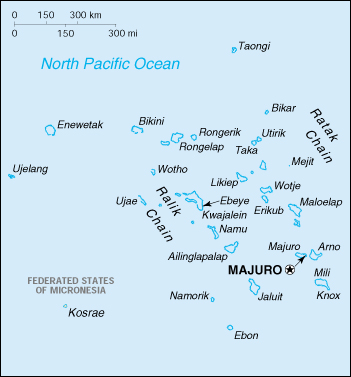
Geography of Marshall Islands
Location: Oceania, group of atolls and reefs in the North Pacific Ocean, about one-half of the way from Hawaii to Papua New Guinea
Geographic coordinates: 9 00 N, 168 00 E
Area:
total: 181.3 sq km
land: 181.3 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: includes the atolls of Bikini, Enewetak, and Kwajalein
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 370.4 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: wet season from May to November; hot and humid; islands border typhoon belt
Terrain: low coral limestone and sand islands
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: unnamed location on Likiep 10 m
Natural resources: phosphate deposits, marine products, deep seabed minerals
Land use:
arable land: 0%
permanent crops: 60%
permanent pastures: 0%
forests and woodland: 0%
other: 40%
Natural hazards: occasional typhoons
Environment – current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Geography – note: two archipelagic island chains of 30 atolls and 1,152 islands; Bikini and Enewetak are former US nuclear test sites; Kwajalein, the famous World War II battleground, is now used as a US missile test range.
People of Marshall Islands
Two-thirds of the nation’s population lives in Majuro and Ebeye. The outer islands are sparsely populated due to lack of employment opportunities and economic development.
The Marshallese are of Micronesian origin, which is traced to a combination of peoples who emigrated from Southeast Asia in the remote past. The matrilineal Marshallese culture revolves around a complex system of clans and lineages tied to land ownership.
Virtually all Marshallese are Christian, most of them Protestant. Other Christian denominations include Roman Catholic, Seventh-day Adventist, Mormon, Salvation Army, and Jehovah’s Witness. A small Bahai community also exists.
Both Marshallese and English are official languages. English is spoken by most of the urban population. However, both the Nitijela (parliament) and national radio use Marshallese.
The public school system provides education through grade 12, although admission to secondary school is selective. The elementary program employs a bilingual/bicultural curriculum. English is introduced in the fourth grade. There is one post-secondary institution in the Marshall Islands–the College of the Marshall Islands.
Population: 59,071 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 49.29% (male 17,808; female 17,101)
15-64 years: 48.61% (male 17,573; female 16,853)
65 years and over: 2.1%
Population growth rate: 3.88%
Birth rate: 45.07 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 6.23 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 39.82 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 65.84 years
male: 64.04 years
female: 67.73
Total fertility rate: 6.55 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Marshallese (singular and plural)
adjective: Marshallese
Ethnic groups: Micronesian
Religions: Christian (mostly Protestant)
Languages: English (universally spoken and is the official language), two major Marshallese dialects from the Malayo-Polynesian family, Japanese
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 93%
male: 100%
female: 88% (1980 est.)
Marshall Islands Economy
Economy – overview: The United States Government assistance is the mainstay of this tiny island economy. Agricultural production is concentrated on small farms, and the most important commercial crops are coconuts, tomatoes, melons, and breadfruit. Small-scale industry is limited to handicrafts, fish processing, and copra. The tourist industry, now a small source of foreign exchange employing less than 10% of the labor force, remains the best hope for future added income. The islands have few natural resources, and imports far exceed exports. Under the terms of the Compact of Free Association, the US provides roughly $65 million in annual aid. Negotiations were underway in 1999 for an extended agreement. Government downsizing, drought, a drop in construction, and the decline in tourism and foreign investment due to the Asian financial difficulties caused GDP to fall in 1996-98.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $105 million (1998 est.), supplemented by approximately $65 million annual US aid.
GDP – real growth rate: -5% (1998 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $1,670 (1998 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 15%
industry: 13%
services: 72% (1995)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 5% (1997)
Unemployment rate: 16% (1991 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $80.1 million
expenditures: $77.4 million, including capital expenditures of $19.5 million (FY95/96 est.)
Industries: copra, fish, tourism, craft items from shell, wood, and pearls, offshore banking (embryonic)
Electricity – production: 57 million kWh (1994)
Electricity – consumption: 57 million kWh (1994)
Agriculture – products: coconuts, cacao, taro, breadfruit, fruits; pigs, chickens
Exports: $28 million (f.o.b., 1997 est.)
Exports – commodities: fish, coconut oil, fish, trochus shells
Exports – partners: United States, Japan, Australia
Imports: $58 million (f.o.b., 1997 est.)
Imports – commodities: foodstuffs, machinery and equipment, fuels, beverages and tobacco
Imports – partners: United States, Japan, Australia, NZ, Guam, Singapore
Debt – external: $125 million (FY96/97 est.)
Economic aid – recipient: approximately $65 million annually from the United States
Currency: 1 United States dollar (US$) = 100 cents
Map of Marshall Islands