Facts About Saint Lucia
Background: The island, with its fine natural harbor at Castries, was contested between England and France throughout the 17th and early 18th centuries (changing possession 14 times); it was finally ceded to the UK in 1814. Self-government was granted in 1967 and independence in 1979.
Government type: Westminster-style parliamentary democracy
Capital: Castries
Currency: 1 East Caribbean dollar (XCD) = 100 cents
Geography of Saint Lucia
Location: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Geographic coordinates: 13 53 N, 60 68 W
Area:
total: 620 sq km
land: 610 sq km
water: 10 sq km
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 158 km
Maritime claims: 200 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical, moderated by northeast trade winds; dry season from January to April, rainy season from May to August
Terrain: volcanic and mountainous with some broad, fertile valleys
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point: Mount Gimie 950 m
Natural resources: forests, sandy beaches, minerals (pumice), mineral springs, geothermal potential
Land use:
arable land: 8%
permanent crops: 21%
permanent pastures: 5%
forests and woodland: 13%
other: 53% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 10 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hurricanes and volcanic activity
Environment – current issues: deforestation; soil erosion, particularly in the northern region
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Geography – note: the twin Pitons (Gros Piton and Petit Piton), striking cone-shaped peaks south of Soufriere, are one of the scenic natural highlights of the Caribbean.
People of Saint Lucia
St. Lucia’s population is predominantly of African and mixed African-European descent, with small East Indian and European minorities. English is the official language, although many St. Lucians speak a French patois. Ninety percent of the population is Roman Catholic, a further reflection of early French influence on the island. The population of just over 147,000 is evenly divided between urban and rural areas, although the capital, Castries, contains more than one-third of the population. Despite a high emigration rate, the population is growing rapidly, about 1.6% per year.
Population: 166,312 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 32.13%
15-64 years: 62.59%
65 years and over: 5.28%
Population growth rate: 1.23%
Birth rate: 21.8 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 5.36 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: -4.15 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 15.22 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 72.57 years
male: 69 years
female: 76.39 years
Total fertility rate: 2.38 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: Saint Lucian(s)
adjective: Saint Lucian
Ethnic groups: black 90%, mixed 6%, East Indian 3%, white 1%
Religions: Roman Catholic 90%, Protestant 7%, Anglican 3%
Languages: English (official), French patois
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over has ever attended school
total population: 67%
male: 65%
female: 69% (1980 est.)
History of Saint Lucia
St. Lucia’s first known inhabitants were Arawaks, believed to have come from northern South America 200-400 A.D. Numerous archaeological sites on the island have produced specimens of the Arawaks’ well-developed pottery. Caribs gradually replaced Arawaks during the period 800-1000 A.D.
Europeans first landed on the island in either 1492 or 1502 during Spain’s early exploration of the Caribbean. The Dutch, English, and French all tried to establish trading outposts on St. Lucia in the 17th century but faced opposition from hostile Caribs.
The English, with their headquarters in Barbados, and the French, centered on Martinique, found St. Lucia attractive after the sugar industry developed in 1765. Britain eventually triumphed, with France permanently ceding St. Lucia in 1815. In 1838, St. Lucia was incorporated into the British windward islands administration, headquartered in Barbados. This lasted until 1885, when the capital was moved to Grenada.
St. Lucia’s 20th-century history has been marked by increasing self-government. A 1924 constitution gave the island its first form of representative government, with a minority of elected members in the previously all-nominated legislative council. Universal adult suffrage was introduced in 1951, and elected members became a majority of the council. Ministerial government was introduced in 1956, and in 1958 St. Lucia joined the short-lived West Indies Federation, a semi-autonomous dependency of the United Kingdom. When the federation collapsed in 1962, following Jamaica’s withdrawal, a smaller federation was briefly attempted. After the second failure, the United Kingdom and the six windward and leeward islands–Grenada, St. Vincent, Dominica, Antigua, St. Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla, and St. Lucia–developed a novel form of cooperation called associated statehood.
As an associated state of the United Kingdom from 1967 to 1979, St. Lucia had full responsibility for internal self-government but left its external affairs and defense responsibilities to the United Kingdom. This interim arrangement ended on February 22, 1979, when St. Lucia achieved full independence. St. Lucia continues to recognize Queen Elizabeth II as titular head of state and is an active member of the Commonwealth. The island continues to cooperate with its neighbors through the Caribbean community and common market (CARICOM), the East Caribbean Common Market (ECCM), and the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
Saint Lucia Economy
Economy – overview: The recent changes in the EU import preference regime and the increased competition from Latin American bananas have made economic diversification increasingly important in Saint Lucia. Improvement in the construction sector and growth of the tourism industry helped expand GDP in 1998-99. The agriculture sector registered its fifth year of decline in 1997 primarily because of a severe decline in banana production. The manufacturing sector is the most diverse in the Eastern Caribbean, and the government is beginning to develop regulations for the small offshore financial sector.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $700 million (2000 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: 0.5% (2000 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $4,500 (2000 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 10.7%
industry: 32.3%
services: 57% (1996 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 2.5% (2000 est.)
Labor force: 43,800
Labor force – by occupation: agriculture 43.4%, services 38.9%, industry and commerce 17.7% (1983 est.)
Unemployment rate: 15% (1996 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $141.2 million
expenditures: $146.7 million, including capital expenditures of $25.1 million (FY97/98 est.)
Industries: clothing, assembly of electronic components, beverages, corrugated cardboard boxes, tourism, lime processing, coconut processing
Industrial production growth rate: -8.9% (1997 est.)
Electricity – production: 110 million kWh (1999)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0%
nuclear: 0%
other: 0% (1999)
Electricity – consumption: 102.3 million kWh (1999)
Agriculture – products: bananas, coconuts, vegetables, citrus, root crops, cocoa
Exports: $68.3 million (2000 est.)
Exports – commodities: bananas 41%, clothing, cocoa, vegetables, fruits, coconut oil
Exports – partners: UK 50%, US 24%, Caricom countries 16% (1995)
Imports: $319.4 million (2000 est.)
Imports – commodities: food 23%, manufactured goods 21%, machinery and transportation equipment 19%, chemicals, fuels
Imports – partners: US 36%, Caricom countries 22%, UK 11%, Japan 5%, Canada 4% (1995)
Debt – external: $131.6 million (1998)
Economic aid – recipient: $51.8 million (1995)
Currency: 1 East Caribbean dollar (XCD) = 100 cents
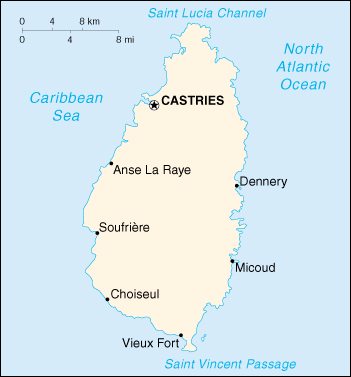
Map of Saint Lucia