Facts About the United States
Background: Britain’s American colonies broke with the mother country in 1776 and were recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783. During the 19th and 20th centuries, 37 new states were added to the original 13 as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired a number of overseas possessions. The two most traumatic experiences in the nation’s history were the Civil War (1861-65) and the Great Depression of the 1930s. Buoyed by victories in World Wars I and II and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the US remains the world’s most powerful nation-state. The economy is marked by steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology.
Form of Government: Federal republic
Capital: Washington, D.C.
Currency: 1 United States dollar (US$) = 100 cents
Geography of the United States
Location: North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico
Geographic coordinates: 38 00 N, 97 00 W
Area:
total: 9,629,091 sq km
land: 9,158,960 sq km
water: 470,131 sq km
note: includes only the 50 states and District of Columbia
Area – comparative: about one-half the size of Russia; about three-tenths the size of Africa; about one-half the size of South America (or slightly larger than Brazil); slightly larger than China; about two and one-half times the size of Western Europe
Land boundaries:
total: 12,248 km
border countries: Canada 8,893 km (including 2,477 km with Alaska), Cuba 29 km (US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay), Mexico 3,326 km
note: Guantanamo Naval Base is leased by the US and thus remains part of Cuba
Coastline: 19,924 km
Climate: mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains.
Terrain: vast central plain, mountains in west, hills and low mountains in east; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii.
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Death Valley -86 m
highest point: Mount McKinley 6,194 m
Natural resources: coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber
Land use:
arable land: 19%
other: 81% (1998 est.)
Irrigated land: 214,000 sq km (1998 est.)
Natural hazards: tsunamis, volcanoes, and earthquake activity around Pacific Basin; hurricanes along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts; tornadoes in the Midwest and southeast; mud slides in California; forest fires in the west; flooding; permafrost in northern Alaska, a major impediment to development.
Environment – current issues: air pollution resulting in acid rain in both the US and Canada; the US is the largest single emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels; water pollution from runoff of pesticides and fertilizers; very limited natural fresh water resources in much of the western part of the country require careful management; desertification.
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Hazardous Wastes
Geography – note: world’s third-largest country by size (after Russia and Canada) and by population (after China and India); Mt. McKinley is highest point in North America and Death Valley the lowest point on the continent.
People of the United States
Population: 295,734,134 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 21%
15-64 years: 66.4%
65 years and over: 12.6%
Population growth rate: 0.89%
Birth rate: 14.1 births/1,000 population
Death rate: 8.7 deaths/1,000 population
Net migration rate: 3.5 migrant(s)/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate: 6.69 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 77.4 years
male: 74.5 years
female: 80.2 years
Total fertility rate: 2.07 children born/woman
Nationality:
noun: American(s)
adjective: American
Ethnic groups: white 77.1%, black 12.9%, Asian 4.2%, Amerindian and Alaska native 1.5%, native Hawaiian and other Pacific islander 0.3%, other 4% (2000)
note: a separate listing for Hispanic is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean a person of Latin American descent (especially of Cuban, Mexican, or Puerto Rican origin) living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (white, black, Asian, etc.)
Religions: Protestant 56%, Roman Catholic 28%, Jewish 2%, other 4%, none 10% (1989)
Languages: English, Spanish (spoken by a sizable minority)
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97%
male: 97%
female: 97% (1979 est.)
United States Economy
Economy – overview: The United States has the largest and most technologically powerful economy in the world, with a per capita GDP of $36,300. In this market-oriented economy, private individuals and business firms make most of the decisions, and government buys needed goods and services predominantly in the private marketplace. US business firms enjoy considerably greater flexibility than their counterparts in Western Europe and Japan in decisions to expand capital plant, lay off surplus workers, and develop new products. At the same time, they face higher barriers to entry in their rivals’ home markets than the barriers to entry of foreign firms in US markets. US firms are at or near the forefront in technological advances, especially in computers and in medical, aerospace, and military equipment, although their advantage has narrowed since the end of World War II. The onrush of technology largely explains the gradual development of a “two-tier labor market” in which those at the bottom lack the education and the professional/technical skills of those at the top and, more and more, fail to get comparable pay raises, health insurance coverage, and other benefits. Since 1975, practically all the gains in household income have gone to the top 20% of households. The years 1994-2000 witnessed solid increases in real output, low inflation rates, and a drop in unemployment to below 5%. The year 2001 witnessed the end of the boom psychology and performance, with output increasing only 0.3% and unemployment and business failures rising substantially. The response to the terrorist attacks of September 11 showed the remarkable resilience of the economy. Moderate recovery is expected in 2002, with the GDP growth rate rising to 2.5% or more. A major short-term problem in first half 2002 was a sharp decline in the stock market, fueled in part by the exposure of dubious accounting practices in some major corporations. Long-term problems include inadequate investment in economic infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, sizable trade deficits, and stagnation of family income in the lower economic groups.
GDP: purchasing power parity – $10.082 trillion (2001 est.)
GDP – real growth rate: 4.1% (1999 est.), 5% (2000 est.), 0.3% (2001 est.)
GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $36,300 (2001 est.)
GDP – composition by sector:
agriculture: 2%
industry: 18%
services: 80% (2001)
Population below poverty line: 12.7% (1999 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 1.8%
highest 10%: 30.5% (1997)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 2.2% (1999), 3.4% (2000), 2.8% (2001)
Labor force: 141.8 million (includes unemployed) (2001)
Labor force – by occupation: managerial and professional 31%, technical, sales and administrative support 28.9%, services 13.6%, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and crafts 24.1%, farming, forestry, and fishing 2.4% (2001)
note: figures exclude the unemployed
Unemployment rate: 4.2% (1999), 4% (2000), 5% (2001)
Budget:
revenues: $1.828 trillion
expenditures: $1.703 trillion (1999)
Industries: leading industrial power in the world, highly diversified and technologically advanced; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, mining
Industrial production growth rate: 5.6% (2000 est.), -3.7% (2001 est.)
Electricity – production: 3,799.944 billion kWh (2000)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel: 70.76%
hydro: 7.19%
nuclear: 19.84%
other: 2.21% (2000)
Electricity – consumption: 3.45 trillion kWh (1999), 3.613 trillion kWh (2000)
Electricity – exports: 14.829 billion kWh (2000)
Electricity – imports: 48.879 billion kWh (2000)
Agriculture – products: wheat, other grains, corn, fruits, vegetables, cotton; beef, pork, poultry, dairy products; forest products; fish
Exports: $776 billion (f.o.b., 2000 est.), $723 billion (f.o.b., 2001 est.)
Exports – commodities: capital goods, automobiles, industrial supplies and raw materials, consumer goods, agricultural products
Exports – partners: Canada 22.4%, Mexico 13.9%, Japan 7.9%, UK 5.6%, Germany 4.1%, France, Netherlands (2001)
Imports: $1.223 trillion (f.o.b., 2000 est.), $1.148 trillion (f.o.b., 2001 est.)
Imports – commodities: crude oil and refined petroleum products, machinery, automobiles, consumer goods, industrial raw materials, food and beverages
Imports – partners: Canada 19%, Mexico 11.5%, Japan 11.1%, China 8.9%, Germany 5.2%, UK, Taiwan (2001)
Debt – external: $862 billion (1995 est.)
Economic aid – donor: ODA, $6.9 billion (1997)
Currency: 1 United States dollar (US$) = 100 cents
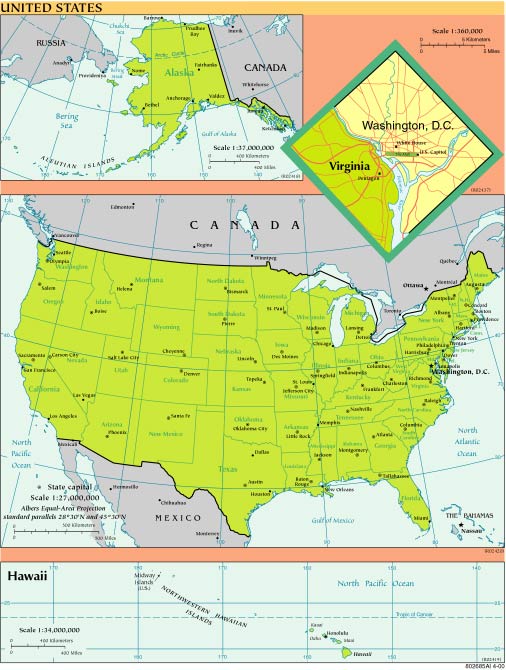
Map of the United States